Scripting Outlet Switching and Energy Measurements
Share
Quickly integrate SynLink functionality into any system with an enterprise set of networking protocols and well documented APIs.
HTTP(S) API, SSH/Serial/Telnet CLI, and SNMP are programming interfaces which allow scripting and integration within larger systems. See examples of API usage with these programming interfaces.
- SynLink Smart PDU
- Network Configured/Connected Setup (Quick Start Guide)
HTTP(S) API Usage
The following examples use CURL to issue HTTP requests.
NodeJS API Wrapper Library is available
Python API Wrapper Library is available
Personal Access Token Authentication
Personal Access Token authentication involves manually creating a personal access token and using it in each request to the SynLink HTTP API.
Get access to HTTP API through PATs (Personal Access Tokens)


curl -H "Authorization: Bearer 2bCDp4lqfKEFl8r6l4s" http://192.168.1.100/api/device
Basic HTTP Authentication
Looking to have backwards compatibility with NetBooter products? Enable HTTP Basic Authentication
In the context of an HTTP transaction, basic access authentication is a method for an HTTP user agent (e.g. a web browser) to provide a user name and password when making a request. In basic HTTP authentication, a request contains a header field in the form of Authorization: Basic <credentials>;
Default: Basic HTTP Authentication denied
Navigate to Network -> Web (/network/web) to enable Basic Authentication.
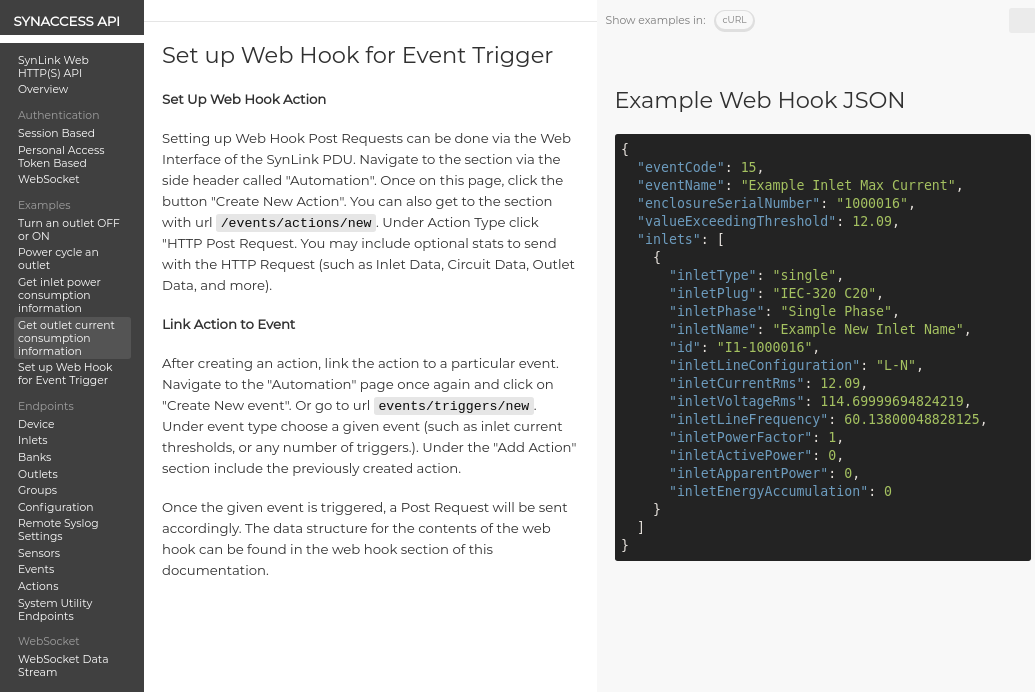
Get Inlet Power Consumption Information
Inlet consumption information can be found with endpoint /api/inlets. This will return an array of inlets. For standard inlet PDU configurations, a single inlet object will be found inside this array. If the PDU is configured as an ATS pdu, or a dual circuit PDU, there will be two inlets.
curl 'http://192.168.1.100/api/inlets' \
--header 'Authorization: Bearer rKKHIKivalp6ihp6e09'
[
{
"inletType": "single",
"inletPlug": "IEC-320 C20",
"inletPhase": "Single Phase",
"inletName": "Example New Inlet Name",
"id": "I1-1000016",
"inletLineConfiguration": "L-N",
"inletCurrentRms": 0,
"inletVoltageRms": 114.69999694824219,
"inletLineFrequency": 60.13800048828125,
"inletPowerFactor": 1,
"inletActivePower": 0,
"inletApparentPower": 0,
"inletEnergyAccumulation": 0
}
]
Turn Outlets On or Off
curl 'http://192.168.1.100/api/outlets/1-1200568' \
--request "PUT" \
--header 'Authorization: Bearer rKKHIKivalp6ihp6e09' \
--data '{ "state":"ON" }'
SSH and Serial Command Line Interface Usage
Access SSH or Telnet with username and password
Execute the ssh command with username and IP address separated by an @. A prompt for admin password will appear. Once properly authenticated, SynLink Shell Help Menu will appear.
Full Examples and Windows 10 Examples
$ ssh [email protected]
The authenticity of host '192.168.1.100 (192.168.1.100)' can't be established.
ECDSA key fingerprint is SHA256:VZMUPw2MrIA3d8797SDEzuWZRxJAo9bLMMUO/Jw.
Are you sure you want to continue connecting (yes/no)?
[email protected]'s password:
-----------------------
SynLink Shell Help Menu
-----------------------
Usage: [command] [options...]
Press Tab to autocomplete commands
Commands
[n]etwork Show and configure network info
[s]ystem Show and Configure PDU power, control, sensors, etc
[set]tings Manage PDU settings
[m]odem Access a connected modem
[l]ogs See various logs
ping [host] Send ping to specified host
[h]elp Returns this message
[ex]amples Common example commands
[exit] Exits SynLink Shell
SynLink> Accessing SSH with Public Keys
Configure SSH for trusted devices to skip username/password authentication.



Scripting SSH with Command Line Interface
Pass commands to SSH as arguments. Use tab to autocomplete words.
Return inlet information in human readable format
$ ssh [email protected] "system inlet status"
-----------------
Inlet Information
-----------------
Inlet Plug | IEC-320 C20R
Inlet Name | IEC-320 C20R Inlet
Inlet ID | I1-1000036
Inlet Line | L-N
Energy Accumulation | 6.73 kWh
Current RMS | 0.38 A
Voltage RMS | 116.10 V
Line Frequency | 60.16 Hz
Power Factor | 0.96
Active Power | 42.29 W
Apparent Power | 43.96 VA
Return device information in JSON format
$ ssh [email protected] "system inlet json"
[
{
"inletType":"single",
"inletPlug":"IEC-320 C20R",
"inletPhase":"Single Phase",
"inletName":"IEC-320 C20R Inlet",
"id":"I1-1000036",
"inletLineConfiguration":"L-N",
"inletCurrentRms":0.38119998574256897,
"inletVoltageRms":116.19999694824219,
"inletLineFrequency":60.13800048828125,
"inletPowerFactor":0.96274548768997192,
"inletActivePower":42.639999389648438,
"inletApparentPower":44.290000915527344,
"inletEnergyAccumulation":6.7277789115905762
}
]
Return inlet information in JSON format and parse for Inlet Current RMS
Requires jq (json parsing tool)
$ ssh [email protected] "system inlet json" | jq .[0].inletCurrentRms
0.37869998812675476
Access Serial CLI
Get tty configuration:
stty -F /dev/ttyUSB0
Change baud rate:
stty -F /dev/ttyUSB0 115200
Write to Serial Port:
echo "system status" > /dev/ttyUSB0
Read from Serial Port:
cat /dev/ttyUSB0
Set Outlet Off
Configure tty with appropriate configurations beforehand
Identify outlet ID beforehand by printing list of outlets: system outlet status
Requires pre login to be able to issue commands.
user@host:~$ echo "system outlet set outlet_state 1-100001 OFF" > /dev/ttyUSB0
or
user@host:~$ sudo sh -c "echo 'system outlet set outlet_state 1-100001 OFF' >> /dev/ttyUSB0"
Get Inlet Current RMS with SNMP
user@host:~$ snmpget -v2c -c public 192.168.1.100 .1.3.6.1.4.1.21728.4.2.1.1.17.1
SYNLINK-MIB::inletCurrentRms.1 = INTEGER: 38
Set Outlet State with SNMP
user@host:~$ snmpset -v2c -c private 192.168.1.100 .1.3.6.1.4.1.21728.4.5.1.1.7.1 i 0
SYNLINK-MIB::outletState.1 = INTEGER: open(0)

